Tinea (Ringworm)
What is tinea (ringworm)?
Tinea is a superficial skin infection caused by a group of fungi collectively called the dermatophytes. These fungi have the ability to infect the outermost cornified layers of the skin, hair or nails. Humidity and moisture provide a favorable environment for the fungi, making infections more common in skin folds, the groin or between the toes. These infections are classified according to location:
- Tinea capitis — scalp
- Tinea faciei — face
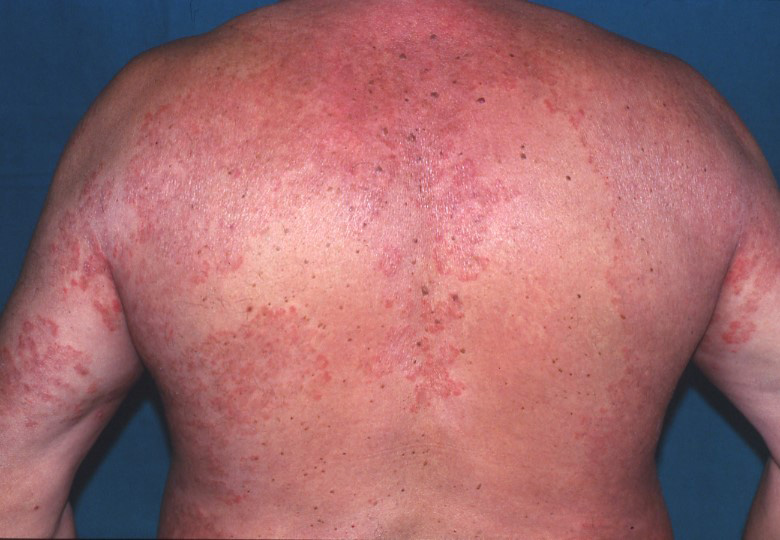
- Tinea corporis — trunk and extremities
- Tinea cruris — groin
- Tinea manuum and Tinea pedis — hands and feet
- Tinea unguium or Onychomycosis — nails
 |
| Zoom In |
What does it look like?
Tinea infections cause itchy and scaly lesions. Patients with tinea capitis have a defined area of hair loss as the infected hair become very brittle and break easily. Skin infections often manifest as round scaly patches with reddish raised borders. Vesicles and pustules may also be seen along the borders of these well-demarcated circular lesions.
How can one get tinea?
Tinea may be spread through direct contact from one person to another (anthrophilic) or from an infected animal or pet (zoophilic). The infection can also be acquired indirectly through infected exfoliated skin or hair in clothes, hairbrushes, towels and linen. The fungal organisms that cause tinea belong to the genera Trichophyton, Microsporum or Epidermophyton.
Who can get tinea?
This superficial fungal infection can affect anyone at any age. Tinea capitis is more commonly seen in children, but can also been seen in adults. Tinea cruris, pedis and oncychomycosis are mostly seen in adults.
How is tinea diagnosed?
Doctors may suspect tinea infection by its appearance. To confirm this diagnosis, scrapings of the skin, scalp or nail may be treated with potassium hydroxide and examined under the microscope. Sometimes, these scrapings may be sent to a lab for fungal culture to positively identify the species of the causative organism.
How do you treat tinea?
Once diagnosed, tinea may be treated using topical anti-fungal medications like clotrimazole, ketoconazole and terbinafine. Oral anti-fungal drugs may be given for extensive disease. Nail infections (onychomycosis) and tinea capitis (scalp) usually do not respond to topical therapy and may require oral treatment. The lesions typically resolve without complications within 2 to 4 weeks of treatment.
Recommended websites:




